Using Global Patent Trends in Smart Manufacturing to Develop an Informed and Effective IP Strategy
In today’s global economy, product research and development (R&D) has historically been concentrated in the U.S. and China. However, these efforts are beginning to decentralize and spread into new regions, such as Japan and South Korea. This geographic shift in R&D investment is reflected in the increasing number of newly filed patent applications, each of which seeks protection of an invention in a specific country or jurisdiction. Below we discuss patent filing trends in smart manufacturing to inform the R&D strategies of today’s top decision makers in this critical sector.
Introduction
Engineers and scientists of leading companies are constantly inventing new solutions to problems. This is particularly true in industries like smart manufacturing, which are core to modern economies. One option for seeking protection of an invention is to file a patent application related to that invention. This patent application is filed in one or more patent offices around the world. There is no ‘international’ patent, so companies must pick and choose which countries to pursue protection in.
For example, a company may invest in developing a new product, and then file a patent application when its engineering team has succeeded in that development. The company may decide to file the patent application in the U.S., because that is the main consumer market for the product, and in China, because that is the main producing market for the product. Having patent protection in China would enable action against competing producers, and having protection in the U.S. would enable action against competing resellers.
Patent filings are generally publicly available after a certain period of time (typically 18 months). Still, the point at which a patent filing becomes publicly available is often well before the invention described in the patent filing becomes known to competitors. Taking our example above, the patent application describing the product may become publicly available long before the product is ever sold (or even produced). Thus, reactively studying the competitive landscape without considering patent trends creates a significant blind spot.
By following trends in patent filings, observers can gain invaluable insights on their competitors. Not only will patent filings give a raw representation of the amount of R&D directed to a particular country or by a specific entity, but detailed patent filing information can even be leveraged to gain insights that are tailored to a particular technology area. In the analysis below, we identify the key markets and challenges that are shaping the smart manufacturing landscape. We also discuss the most active technology areas within smart manufacturing and provide some concrete examples of how patent filing data can be used to answer specific questions and inform strategic decisions.
Framework for Categorizing and Analyzing Filing Trends in Smart Manufacturing
Patent applications are typically classified according to technology area. “Smart manufacturing” is an inherently amorphous term, and lacks a commonly accepted industry definition. Consequently, studying patent filing trends in smart manufacturing is difficult and has historically produced results that are more academic than actionable. Smart manufacturing encompasses a wide range of technologies that enable the integration of physical and digital systems, such as sensors, robotics, artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and blockchain. Therefore, any attempt to define smart manufacturing must account for its multidimensional and dynamic nature.
For the purposes of our analysis, we created a framework for identifying and isolating a subset of patent filings within the “smart manufacturing” technology sector. This framework is intended to be relatively broad so as to accurately reflect current industry viewpoints and provide meaningful insights. Accordingly, the resulting subset includes patent filings across numerous technology areas including, for example, additive manufacturing, warehouse storage, and the management and control of devices including through the use of the Internet of Things. This definition is not meant to be exhaustive or exclusive, but rather to provide a reasonable and practical framework for identifying and categorizing patent filings related to smart manufacturing.
Using this definition, we applied a combination of keyword searches, patent classification codes, and manual review to filter out irrelevant patent filings and isolate those that are most relevant to smart manufacturing. The resulting subset of patent filings reflects the diversity and breadth of smart manufacturing technologies, as well as the innovation efforts and strategies of various entities in this sector.
Analysis of Results
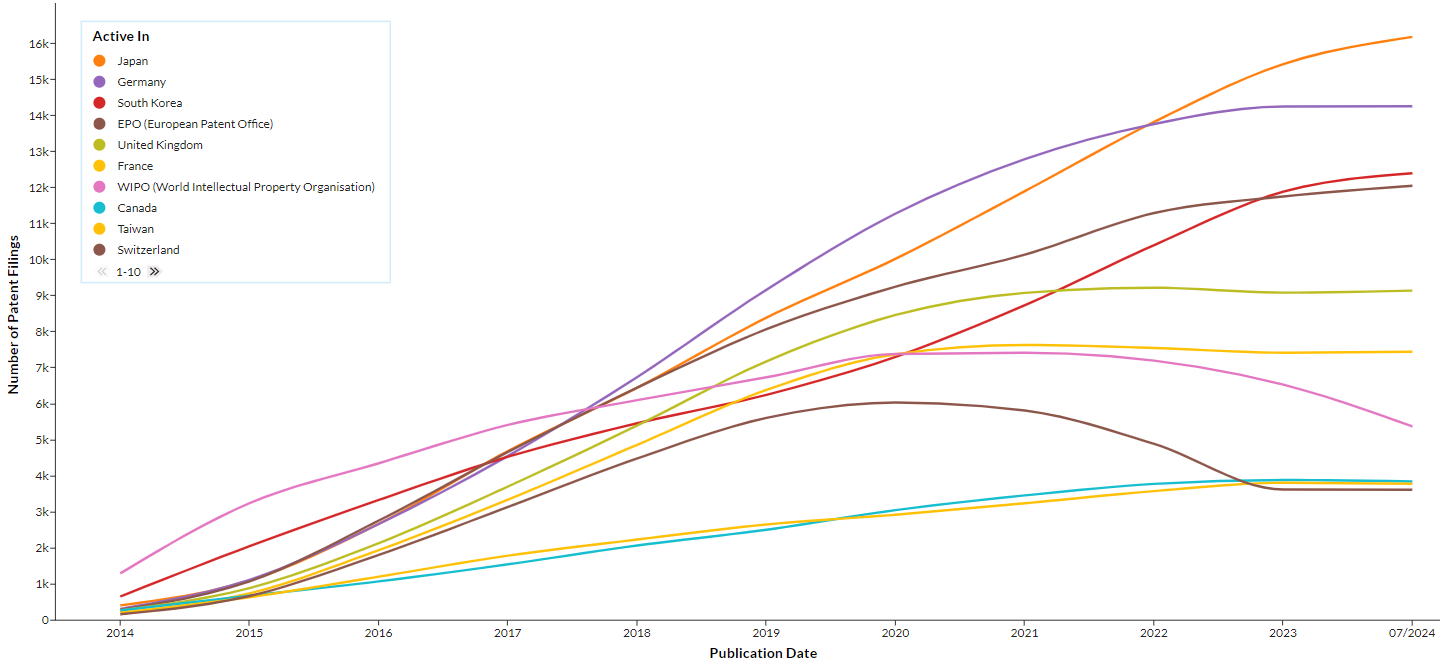
First, we examine where smart manufacturing patent filings have occurred over the past 10 years.1 Immediately noticeable is a significant recent growth in patent filings. For example, China and the U.S. have experienced increases in smart manufacturing patent filings of 579% and 212%, respectively. For context, the increase in total patent filings (not just smart manufacturing ones) in China and the U.S. during that same time period is only 196% and 157%, respectively. This indicates intense development efforts underway in these key markets. Many companies have significant manufacturing operations in China and the U.S., and these jurisdictions are often some of the most popular for patent filings. The immense number of filings in China and the U.S. underscore the need to have a patent and R&D strategy that prioritizes these markets.
While not occurring at anywhere near the same rate, many countries have also experienced recent increases in smart manufacturing patent filings. In particular, the rise of filings in Japan and South Korea is notable. Many companies have manufacturing hubs in Japan and South Korea, so filings in these jurisdictions often makes sense. One driving factor behind the increases in Japan and South Korea during the last 10 years may be that both countries joined the Global Patent Prosecution Highway (GPPH) in 2014, a program which often expedites the process for obtaining a patent.
When China and the U.S. are excluded, interesting trends in smart manufacturing patent filings emerge. Notably, international (“WIPO”) patent filings, which themselves do not grant rights but are often used as a springboard for filing patent applications in numerous countries, have become less popular in recent years. Another trend is that filings in highly developed countries like Japan, South Korea, and Europe have significantly increased.
However, there is more to these numbers than meets the eye. A significant difference often exists between the number of patent filings and the number of patents granted. This is because Patent Offices will often reject patent filings as not claiming a new or non-obvious invention. This is particularly true in technology areas like smart manufacturing that are undergoing intense ongoing development.
Our analysis revealed that while a large number of smart manufacturing patent filings have occurred in China, a relatively small number of smart manufacturing patents have been granted in China. As shown below, the U.S. is the leader in smart manufacturing patent grants (even despite the significantly larger number of patent filings in China). This trend underscores the need for smart manufacturing companies to invest in the construction of robust U.S. patent portfolios.
Outside of the U.S. and China, patent grant trends indicate that Japan dominates other jurisdictions, although there have been relatively significant recent increases in patent grants in Germany, Taiwan, and the U.K. The increase in patent grants in the U.K. likely reflects the impact of Brexit, but the increase in the Germany is curious and worth further inspection.
Another way of viewing smart manufacturing patent filing trends is to break the filings down into segments, each of which represents a particular technology. Comparing the charts from 2014 and 2024, below, reveals a significant increase in fabrication-based patent filings while highlighting the continued dominance of computation (controls) based patent filings, which grew almost 85% during that time frame. Paired together, these increases illustrate the trend to seek patent protection for physical hardware as well as software techniques and innovations.
| Smart Manufacturing Segment Sizes in 2014 | Smart Manufacturing Segment Sizes in 2024 |
Other interesting trends have emerged that illustrate the birth and adoption of new manufacturing trends, such as additive manufacturing or additive layer manufacturing (ALM). Patents in the fabrication and plastics engineering segment exploded by 3,293%, from only 349 patent families in 2014 to 11,840 patent families in 2024. Similarly, the fabrication and layered products segment exploded 44,511% from only 18 patent families in 2014, to 8,030 patent families in 2024. These segment increases illustrate a “race to the patent office” to protect new ALM techniques.
R&D Strategies in View of Analysis
The trends in patent filings discussed above provide a quantitative backdrop to the suspicions smart manufacturing insiders have had for many years. China and the U.S. are the dominant markets for R&D, but ongoing reshoring efforts have begun to reshape the landscape. Technology hotspots like Japan and South Korea have embraced smart manufacturing and are becoming an increasing point of focus. In Europe, filings in the U.K. and Germany indicate a more localized approach to manufacturing akin to what has been seen for many years in the U.S. Of course, the upcoming change in Federal administration is primed to impact (and potentially significantly impact) reshoring efforts and will have a significant impact on IP strategies going forward.
Key factors that influence patent filing strategies include the market size and potential of the target regions. According to a report by Grand View Research, the global smart manufacturing market size was valued at USD 254.24 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.9% from 2023 to 2030. The report identifies the Asia Pacific region as the largest market and anticipates it to be the fastest growing. The growth of the smart manufacturing market is driven by various factors, such as the increasing adoption of industrial automation, the rising demand for energy efficiency and environmental sustainability, the growing integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing, and the emergence of new business models and revenue streams.2
Another factor that influences patent filing strategies is the regulatory environment and the legal protection of intellectual property rights in different jurisdictions. According to a report by the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, the U.S. ranks first in the world in “International IP Index,” which “measures how economies empower innovators and creators and whether individual nations and the global marketplace are on the path to shape a brighter future,” followed by the U.K., France, Germany, Sweden, and Japan. China checked in at 24th on the Index. The report evaluates 55 economies based on 50 unique criteria across nine categories, such as patents, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets, enforcement, and systemic efficiency.3
Based on these factors, smart manufacturing companies should tailor their patent filing strategies to align with their business objectives and market opportunities. They should consider the following aspects when deciding where and how to file patent applications:
- The scope and quality of patent protection in different jurisdictions, and the costs and benefits of obtaining and maintaining patents.
- The market potential and demand for smart manufacturing products and services in different regions, and the competitive advantages and disadvantages of entering and operating in those markets.
- The innovation trends and activities of the competitors and potential collaborators in the smart manufacturing sector, and the gaps and opportunities for differentiation and value creation.
- The regulatory requirements and standards for smart manufacturing in different jurisdictions, and the risks and challenges of complying with them.
By following these guidelines, smart manufacturing companies can optimize their patent filing strategies and enhance their R&D performance and market position.
Patents play an important role in protecting a company’s R&D efforts and setting the stage for sustained success for years to come. Decisionmakers should carefully study where their competitors are filing patent applications and where their operations, and their competitors operations, are located. It is relatively easy to adjust patent filing strategies on an ongoing basis, and it is important to consistently reevaluate strategy in order to maximize R&D budgets and secure protection of maximum value. Foley’s regularly published manufacturing insights will continue to serve as a go-to resource for guiding your patent filing strategies.

2024 Manufacturing Manual
As you navigate the rapidly-evolving manufacturing landscape, the pace of change – from digital disruption to supply chain resiliency to the ubiquity of AI – has never been greater. In Foley’s 2024 Manufacturing Manual, authors from diverse practices and perspectives will release weekly articles that provide a comprehensive “end-to-end” analysis of the manufacturing industry’s legal landscape. Our passion is empowering manufacturers to navigate a rapidly changing world with confidence and agility by providing the knowledge, insights, and legal strategies you need to flourish. We hope this Manufacturing Manual helps you unlock new opportunities for growth, innovation, and success.

